Emotions are complex psychological states that involve subjective experiences, physiological responses, and behavioral expressions. They are typically triggered by internal or external stimuli and can range from intense feelings of joy, love, and excitement to negative emotions like anger, fear, and sadness.
Emotions are
characterized by several key features, including their intensity, duration, and
valence (positive or negative). They also involve cognitive processes such as
attention, memory, and appraisal, as well as physiological changes such as
changes in heart rate, breathing, and hormonal activity. Emotions can be
expressed through facial expressions, vocalizations, and body language.
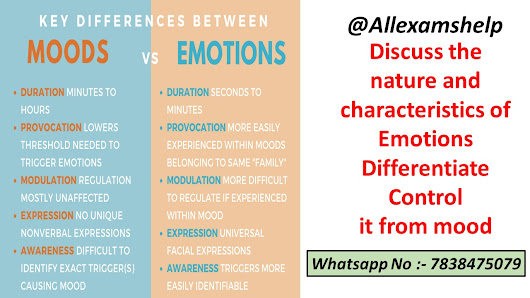
Discuss the nature and
characteristics of emotions Differentiate it from mood and feelings
Moods, on the
other hand, are more generalized emotional states that are not necessarily
linked to a particular event or stimulus. They are longer-lasting than emotions
and can persist for hours, days, or even weeks. Moods are often described in
terms of their valence (positive or negative) and arousal level (high or low).
Feelings are
subjective experiences that arise in response to stimuli or events. They can be
described as a subjective experience of emotions or moods. Unlike emotions,
which are typically intense and short-lived, feelings can be more stable and
enduring. They are often influenced by a person's beliefs, attitudes, and
expectations.
In summary,
emotions are intense, short-lived psychological states that involve
physiological responses and behavioral expressions. Moods are longer-lasting
emotional states that are not necessarily linked to a particular stimulus or
event. Feelings are subjective experiences that can be a reflection of emotions
or moods, but can also be influenced by other factors.
Emotions,
moods, and feelings are interrelated, but they have distinct differences.
Emotions are brief, intense, and typically have a clear cause or trigger.
Moods, on the other hand, are longer-lasting and less intense than emotions.
They are often not tied to a particular event or situation, and can last for
hours, days, or even weeks.
Feelings are
subjective experiences that arise from emotions and moods. They are the
conscious awareness of one's emotional state and can be influenced by personal
experiences, cultural norms, and other contextual factors. For example, sadness
may be an emotion that arises in response to a specific event, such as the loss
of a loved one. The feeling of grief that follows may be a mood that persists
over time, and may be accompanied by a range of other emotions, such as anger
or confusion.
In summary,
emotions are intense, short-lived reactions to specific events or stimuli,
moods are longer-lasting and less intense, and feelings are the conscious
awareness of emotional states.
Emotions are
complex psychological experiences that involve a range of physiological,
cognitive, and behavioral responses to a stimulus or situation. Emotions are
often described as intense feelings that are accompanied by physical
sensations, thoughts, and behaviors. Here are some key characteristics of
emotions:
Subjective
experience: Emotions are personal and subjective experiences that are unique to
each individual. Two people can experience the same event, but have different
emotional responses to it.
Physiological
response: Emotions are associated with physiological changes in the body, such
as changes in heart rate, breathing, and hormone levels. These changes are
often automatic and can be measured using various scientific techniques.
Cognitive component:
Emotions involve cognitive processes, such as perception, attention, and
memory. The way we interpret and evaluate a situation can influence our
emotional response to it.
Behavioral
expression: Emotions are often expressed through behavior, such as facial
expressions, body language, and vocalizations. These behaviors can provide
social cues to others and communicate our emotional state.
Adaptive
function: Emotions serve an adaptive function by helping us respond to
environmental demands and make appropriate decisions. For example, fear can
motivate us to avoid dangerous situations, while happiness can encourage us to
engage in activities that promote well-being.
For SOLVED PDF & Handwritten
WhatsApp No :- 7838475019
Complex and
dynamic: Emotions are complex and dynamic experiences that can change rapidly over
time. They can be influenced by a variety of factors, such as personality,
culture, and social context.
Overall,
emotions are an integral part of the human experience and play a critical role
in our daily lives. Understanding the nature and characteristics of emotions
can help us manage our own emotions and communicate effectively with others.