EVOLUTION
EVOLUTION NOTES CLASS 12: Evolutionary biology is the study of history of life forms
on earth. We must have an understanding of the context of origin of life,i. e.,
evolution of earth, of stars and indeed of the universe itself. The Bing bang theory attempts to explain to
us the origin of universe. It talks of a singular huge explosion unimaginable
in physical terms. The universe expanded and hence, the temperature came down.
Hydrogen and Helium formed sometime later. The gases condensed under
gravitation and formed the galaxies of the present day universe. In the solar system
of the milky way galaxy, earth was supposed to have been formed about 4.5
billion years back. There was no atmosphere on early earth. Primitive
atmosphere had high temperature, stormy storms, and reducing atmosphere,
containing CH4, NH3, H2, etc.
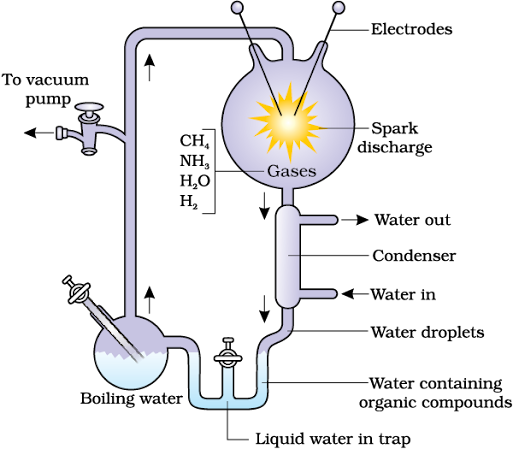
UREY AND MILLER EXPERIMENT
Urey and Miller took the same composites in a unrestricted
beaker along with water vapour at 800 ºC and created an electric discharge.
Conformation of biomolecules similar as amino acids, simple
sugars, fats, etc. was observed in the beaker.
EVOLUTION NOTES CLASS 12:
Theories of Evolution
● The proposition of special creation or godly intervention
was challenged by Charles Darwin.
● He made
compliances on his ocean ¬ trip around the world aboard H.M.S.
Beagle and concluded that all being living forms partake
parallels among themselves and also with other life forms, which was millions
of times ago of which numerous are defunct.
● The evolution of
life forms has been gradational and those life forms better fit in surroundings
that leave more progeny. This is called natural selection and is a mechanism of
evolution..
● Alfred Wallace working in the Malay Archepelago also came
to the same conclusion.
ALSO CHECK:
- BPSC 132 Solved Assignment 2021-22 In Hindi Medium
- BPSC 131 Solved Assignment 2021-22 In English Medi
- BPSC 132 Solved Assignment 2021-22 In English Medium
Human Evolution Class 12 Notes
Evidences of Evolution
· Fossils − They represent plants
and creatures that lived millions of times ago and are now extinct. Different
aged gemstone sediments contain fuds of different life ¬ forms, which
presumably failed during the conformation of the particular deposition.
· Relative anatomy and morphology − It
shows attestations of the parallels and differences between living forms of
moment and that of the Neolithic times. Some of the exemplifications of
relative deconstruction and morphology are
· Homologous organs − All
mammals partake the same pattern of forelimbs. Though they perform different
functions, they're anatomically analogous. This is called divergent evolution and the structures are called homologous
structures (common ancestors).
· Analogous organs − The
brace of organs isn't anatomically analogous, but performs the same function
(e.g., the bodies of butterflies and catcalls). This is called convergent evolution.
· Adaptive melanism − In
England, it was noted that before artificial revolution, the number of white-winged
moths was further than that of dark melanised moth. Still, after
industrialization, there were further of dark melanised moths. The explanation
was that after industrialization, the tree caddies came darker with deposits of
soot and bank and hence, the number of dark moths increased in order to cover
themselves from bloodsuckers while the white-winged ones were easily picked up
by the predators.
· Also,
the pesticide and fungicide resistant plants and creatures and antibiotic resistant
bacteria are some of the attestations that point towards evolution.
Adaptive Radiation
● During his disquisition of the Galapagos islands, Darwin
noticed that there were numerous kinds of finches in the same island.
● They varied from normal seed eating kinds to those that
ate insects.
● This process of evolution starting from a single point
and radiating in different directions is called adaptive radiation.
● The other example for this is the evolution of the
Australian marsupials from a single ancestor. Placental mammals also parade
parallels to their corresponding marsupial. Example placental wolf and the
Tasmanian wolf
● When further than one adaptive radiation occurs in an
insulated geographical area, the miracle is called convergent evolution.
EVOLUTION NOTES CLASS 12
Natural Evolution & Mechanism of
evolution
● According to
Darwin, evolution took place by natural selection.
● The number of life
forms depends upon their capability to multiply and their life span.
● Another aspect of natural selection is the survival of
the fittest, where nature selects the individualities, which are most fit, to
adapt to their environment.
● Branching descent and natural selection are the two important
generalities of Darwin’s proposition of evolution.
● The French
naturalist Lamarck observed that evolution occurs due to the use or disuse of
particular organs or body corridor. For example, giraffe have developed long
necks as a result of attempts to eat leaves grandly over on trees.
● Darwin also observed that variations are heritable and
the species fit to survive the most, leaves more offspring. Hence, the
population’s characteristics change, giving rise to the evolution of new life
forms.
EVOLUTION NOTES CLASS 12:
Mechanism of evolution
● Darwin didn't relatively explain how evolution gave rise
to different species of the same organism.
● Mendel mentioned about heritable factors, which told the
phenotype of an organism.
● Hugo de Vries grounded on his work on evening primrose
suggested that variations passed due to mutations.
● Mutations are
arbitrary and directionless while the variations that Darwin talked about were
small and directional. Hugo de Vries gave the name saltation (single step large mutation) to the mutations which
brought about speciation.
RELATED LINKS:
- ORGANISMS AND POPULATIONS
- Human Health and disease
- REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
- Biodiversity and conservation
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
· The frequency
of circumstance of alleles of a gene in a population remains constant through
generations unless disturbances similar as mutations, non-random mating, etc.
are introduced.
· Genetic
equilibrium (gene pool remains constant) is a state which provides a birth to
measure genetic change.
· Sum aggregate
of all allelic frequencies is 1.
· Individual
frequenness are represented as p and q similar as in a diploid, where p and q
represent the frequency of allele A and a.
· The frequency
of AA is p 2, that of aa is q 2, and that of Aa is 2pq
· Hence,
p 2 + 2pq + q 2 = 1, which is the expansion of (p+q) 2.
· When
the frequencies measured is different from that anticipated, it's reflective of
evolutionary change.
· Hardy
¬ Weinberg equilibrium is affected by
I.
Gene inflow or gene migration
II.
genetic drift (changes being by chance)
III.
Mutation
IV.
Genetic recombination
V.
Natural selection
· Occasionally,
the change in allele frequency is so prominent in the new sample of population
that they come a different species and the original drifted population becomes
the author. This effect is called founder
effect.
· The advantageous
mutations that help in natural selection over the generations give rise to new
phenotypes and affect in speciation.
Evolution short notes
Evolution of Plants and Creatures
Evolution of Plants
· Cellular
life forms passed on earth about 2000 million times ago .
· Some
of these cells had the capability to produce oxygen through responses analogous
to photosynthesis.
· Sluggishly,
single ¬ celled organisms came multicellular.
· Seaweeds
and some plants presumably was around 320 million times agone.
Evolution Notes Class 12 Handwritten Notes
Evolution of Creatures
· Creatures
evolved about 500 million times ago. The first of them to evolve were pets.
· Jawless
fishes evolved around 350 million times ago.
· Some
of the fishes could go on land, and also come back to water. These were the
first amphibians. In 1938, a fish Coelacanth, which was allowed to be defunct,
was caught in South Africa. This variety of fish, called lobefins, is believed
to have evolved into the first amphibians.
· Amphibians
evolved into reptiles. In the coming 200 million times, reptiles of different
sizes dominated the earth. Still, about 65 million times ago, some of them
similar as dinosaurs faded.
· The
first among the mammals were small fury-like mammals.
· During
continental drift when North America joined South America, primitive mammals
suffered, but swelled mammals of Australia survived the same drift because of
lack of competition from other mammals.
EVOLUTION NOTES CLASS 12:
Origin
and Evolution of Man
EVOLUTION NOTES CLASS 12: When we compare the skulls of an adult human being, baby
chimpanzee, and adult chimpanzee, we observe that skull of baby chimpanzee
resembles human being more as compared to adult chimpanzee.