REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
Introduction
Each and every organism can live only for certain period of
time. The period from birth to the natural death of an organism represents its
life span. Life span of a many organisms. Several other organisms are drawn for
which you should find out their life spans and write in the spaces handed.
Examine the life spans of organisms represented. Is n’t it both intriguing and
interesting to note that it may be as short as a many days or as long as a many
thousand times? Between these two axes are the life spans of utmost other
living organisms. Also, a mango tree has a important shorter life and span as
compared to a peepal tree. Whatever be the life span, death of every individual
organism is a certainty, i.e., no existent is immortal, except single-celled
organisms.
REPRODUCTION
IN ORGANISMS
• Life Span
Period from birth till natural death. Every organism lives
only for certain period of time Eg Elephant 60-90 times, Fruit cover 4-5 weeks.
Every organism live only for a certain period of time.
TYPES OF REPRODUCTION
• Asexual reproduction single parent able of producing offspring.
Somatogenic reproduction
• Sexual reproduction
two parents are invovled in producing offspring.
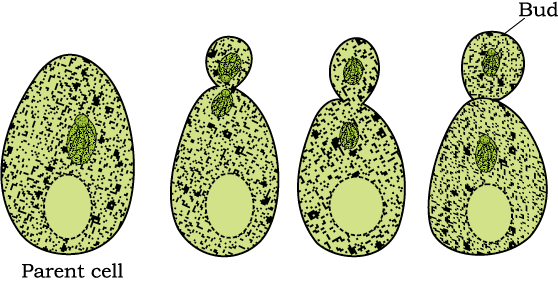
(a) Budding in yeast
(b) Binary fission in amoeba
Modes of asexual Reproduction
• Binary fission: parent body divides into two halves, genetically identical to parent. Amoeba It's simple or irregular.
Asexual reproductive structures:
• Paramecium: Transverse double fission.
Organisms considered immortal
• Multiple fission: parent body divides into numerous son
organisms Plasmodium.
• Budding: son organisms grow from small
kids arising in parent body. Exogenous budding out side the body eg. Hydra,
Incentive.
• Budding in yeast Endogenous budding: inside the
body eg. Gemmule in sponger. Oidia of rhizopus
• Conidia: non-motile, exogenous spores in chains eg.
Fungi.
• Zoospores: bitsy
motile structures eg. Algae.
• In plants: term vegetative reproduction constantly used rather
of asexual reduplication, units of vegetative propagation called vegetative propagules
.eg runner, rhizome, sucker, tuber
neutralize, bulb give rise to new plants
. • All organisms show remarkable similarity. Vast
difference in their reproductive structure. Analogous pattern or phases in
their life cycles.
Vegetative propagules in angiosperms ;
• PHASES OF LIFE SPAN.
•
Juvenile
phase: The phase of growth before reproductive maturity.
•
Reproductive
phase: Reproductive maturity.
•
Ancient
phase: Phase between reproductive maturity and
RELATED LINK:
THE MAIN EVENTS OF SEXUAL CYCLE ARE
i. Pre-fertilization
events
a. Gametogenesis
•
The process of conformation of male and female
gametes by meiosis ( cell- division).
•
Homogamete: (Isogamete):-gametes
analogous eg. Algae
•
Heterogamete (an-isogamete):-morphologically
different gamete, male gamete (antherozoid or sperm), female gamete (egg or
ovum) eg. Mortal.
•
sexuality in organisms: In plants
Bisexual term is used for Homothallic and Monoecious plants Both male and female
reproductive structures in same plants eg. Advanced plants, cucurbits and
coconut.
•
Androgynous term used for
Heterothallic and Dioecious plants: Male and female reproductive-
structure on different plants.
Flowering
plants – male flower – staminate flower and female flower-pistillate flower eg.
papaya and date- win.
•
Creatures – Bisexual term is used for
Hermaphrodite creatures : eg. Earth-worm, Vid-worm, Leech, Sponge.
•
Androgynous creatures have male &
female relations in separate individualities : -e.g. insects, frogs,
human beings
ALSO CHECK:
BPSC 132 Solved Assignment 2021-22 In Hindi Medium
• Cell division during gamete formation:
• Haploid-parent (n) produces
haploid gametes (n) by mitotic division, eg. Monera, fungi, algae and
bryophytes Diploid parent (2n) produces haploid gametes (n) by meiosis division
( retain only one set of chromosomes) and similar technical parent cell is
called meiocyte or gamete mother cell.
b) Gamete transfer : to
grease emulsion.
•
Male gametes substantially motile and female non-motile,
exception many fungi and in algae both gametes are motile in some cases
•
Water medium for gamete transfer-in lower plants.
Large number of male gametes produced to compensate loss
•
Advanced plants, pollen- grains are transferred
by pollination.
•
Fertilization: Fusion of male and female
gametes diploid zygote.
•
Parthenogenesis: development
into new organism without fertilisation eg. Rotifers, honey- notions, some
lizard, raspberry ( lemon).
ii. Fertilization
TWO
TYPES-EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL.
• External fertilization;
outside the body of organism in
external- medium (water) e.g. maturity of algae, fishes, amphibians.
• Advantage:- show
great coincidence between the relations –
1. Release of large number of gametes into girding medium
2. Large number of offspring produced.
• Disadvantage- offspring
vulnerable to bloodsuckers, natural disasters.
Also check:
BPSC 131 Solved Assignment 2021-22 In Hindi Medium
• Internal fertilization:- emulsion
occurs inside female body e.g. maturity of plants and creatures. Egg non-motile
and formed inside female body. Male gamete motile, produced in large figures to
reach egg and fuse with it. In offspring plants, non-motile male gamete carried
to female gamete by pollen- tube.
III. POST-FERTILISATION EVENTS-
Conformation OF ZYGOTE.
•
Zygote: One
celled, diploid, vital link between two generations.
•
External fertilization: zygote
formed in external medium water eg. Frog,
•
Internal fertilization:
zygote formed inside the body eg. Mortal beings. Development of zygote depends
on type of life cycle and terrain. Some develop thick wall ( help damage and
desiccation) & suffer period of rest eg. Algae, fungi.
•
Haplontic life cycle: zygote
(2n) divides by meiosis to form haploid (n) spores.
•
Diplontic life- cycle:- zygote
(2n) divides mitotically, develops into embryo (2n).
•
Oviparous creatures lay eggs out: side
the female body.Eggs can be fertilized/ unfertilized. Fertilized eggs covered
which hard calcareous shell, laid in safe place in the terrain. Unfertilized
eggs laid in water. Illustration-fishes, frogs, reptiles, catcalls
•
Viviparous
creatures: bear and rear the embryo inside female body, give birth to
youthful- bones. Advantage-proper embryonic care, protection, survival chances
of youthful- bones lesser. Example cows, jumbos, mortal beings.
•
Embryogenesis: development
of embryo from zygote by cell division (mitosis) and cell isolation.
• Cell: division increases the number of cells in the developing embryo Cell isolation- groups of cells suffer certain variations for the conformation of different kinds of tissue and organs.
• In flowering plants : zygote formed inside ovule