Tariffs and Customs: Disputes may occur when countries impose tariffs or customs duties on imported goods, making them more expensive and affecting the competitiveness of foreign products.
Subsidies:
Disagreements can arise when countries provide subsidies to their domestic
industries, which may distort international trade by giving an unfair advantage
to local producers.
Intellectual
Property Rights (IPR): Conflicts may occur when countries fail to protect or
enforce intellectual property rights, such as patents, copyrights, and
trademarks, leading to issues of piracy, counterfeiting, and infringement.
Explain the methods of settling the trade disputes along
with advantages and disadvantages
Trade Barriers:
Disputes can arise due to non-tariff barriers, including quotas, embargoes,
licensing requirements, technical standards, and sanitary and phytosanitary
measures, which can impede market access for foreign products.
Dumping:
Disagreements may occur when countries export goods at prices below their
production cost or below the prices in the domestic market, causing harm to
domestic industries in the importing countries.
Negotiations
and Consultations: Countries engage in direct talks and consultations to find
mutually agreeable solutions. This can involve bilateral negotiations or
multilateral discussions through organizations like the World Trade
Organization (WTO).
Mediation: A
neutral third party assists the disputing parties in reaching a resolution by
facilitating negotiations and suggesting potential compromises. Mediation is a
voluntary and non-binding process.
Dispute
Settlement Panels: The WTO has a formal mechanism for resolving trade disputes
through panels composed of experts. Panels examine the case, gather evidence,
and issue a binding decision to settle the dispute.
Arbitration:
Countries can agree to submit their dispute to an independent arbitration
panel. Arbitration involves the parties presenting their arguments and
evidence, and the panel delivers a binding decision.
Negotiations
and consultations promote dialogue and allow countries to find mutually
beneficial solutions without resorting to formal legal procedures.
Mediation
provides a neutral platform for parties to express their concerns and explore
compromises, fostering cooperative relationships.
Dispute
settlement panels and arbitration offer a formal and structured process with
expert analysis, ensuring fairness and predictability in resolving disputes.
Negotiations
and consultations can be time-consuming, and reaching a consensus may prove
challenging, especially when there are significant differences in positions.
Mediation is
non-binding, and parties are not obligated to accept the mediator's
suggestions, which may result in an impasse.
Dispute
settlement panels and arbitration processes can be expensive, requiring
significant resources and time to gather evidence and present arguments.
The enforcement
of decisions can be difficult, particularly if a country refuses to comply with
the ruling or faces political obstacles domestically.
It is important
to note that the effectiveness of each method depends on the willingness of the
disputing parties to engage in good faith negotiations and comply with the
agreed-upon settlement.
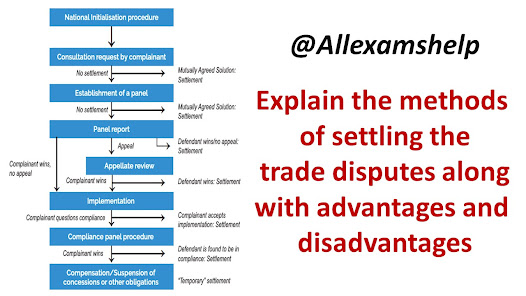
Trade disputes can arise between countries when they have disagreements or conflicts regarding international trade policies, practices, or specific trade-related issues. These disputes can have a significant impact on global trade and economic relations. To settle trade disputes, various methods are available, ranging from negotiations and consultations to formal legal procedures. Here are some common methods used to settle trade disputes:
Negotiation and
Consultation: Often, trade disputes begin with informal negotiations and
consultations between the countries involved. Diplomatic channels and bilateral
or multilateral discussions are used to resolve differences, find common
ground, and reach mutually acceptable solutions. This method emphasizes
dialogue and compromise.
Mediation:
Mediation involves the intervention of a neutral third party who assists the
disputing parties in finding a resolution. The mediator facilitates
negotiations, helps identify common interests, and proposes potential
solutions. The goal is to help the parties reach a mutually agreeable
settlement. Mediation can be voluntary or mandated by trade agreements.
Dispute
Settlement Mechanisms within Trade Agreements: Many trade agreements include
provisions for resolving disputes. These mechanisms typically involve a panel
or tribunal composed of experts in trade law and dispute resolution. Parties
present their cases, and the panel delivers a binding decision. The World Trade
Organization (WTO) has a Dispute Settlement Understanding (DSU) that provides a
formal process for resolving trade disputes among its member countries.
Arbitration:
Arbitration is a method where the disputing parties agree to submit their case
to an independent arbitrator or a panel of arbitrators. The arbitrators consider
the evidence and arguments presented by both parties and issue a binding
decision. Arbitration can be conducted under the rules of international
organizations, such as the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) or the
United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL).
Litigation: In
some cases, trade disputes may be taken to domestic courts or international
judicial bodies. Parties may file lawsuits or complaints seeking legal
remedies. For instance, the WTO's dispute settlement process includes the
option of a panel's ruling being appealed to the WTO's Appellate Body. Domestic
courts can also handle trade disputes, especially when they involve violations
of domestic laws or trade agreements.
Political
Intervention: In certain situations, trade disputes may require political
intervention. High-level discussions and negotiations involving heads of state,
ministers, or other government officials can be employed to find a resolution.
Political pressure or diplomatic solutions can help break deadlocks and pave
the way for compromises.
It's important
to note that the choice of method depends on the nature and severity of the
trade dispute, the preferences of the involved parties, and the legal framework
established by relevant trade agreements. The objective of settling trade
disputes is to achieve a fair and balanced outcome that promotes trade
stability and addresses the concerns of all parties involved.
For SOLVED PDF & Handwritten
WhatsApp No :- 8130208920